Claim Your Offer
Unlock a fantastic deal at www.statisticsassignmenthelp.com with our latest offer. Get an incredible 10% off on all statistics assignment, ensuring quality help at a cheap price. Our expert team is ready to assist you, making your academic journey smoother and more affordable. Don't miss out on this opportunity to enhance your skills and save on your studies. Take advantage of our offer now and secure top-notch help for your statistics assignments.
We Accept
- Understanding the Scope of Statistics Assignments
- Key Steps to Solving SPSS-Based Statistics Assignments
- 1. Comprehend the Assignment Requirements
- 2. Understand the Data Structure
- 3. Conduct Initial Data Exploration
- 4. Choosing the Right Statistical Test
- 5. Performing Power Analysis and Sample Size Calculation
- 6. Conducting Statistical Tests in SPSS
- 7. Interpreting Results Accurately
- 8. Reporting Findings Clearly
- 9. Addressing Non-Parametric Alternatives
- 10. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
- Conclusion
Statistics assignments often require students to analyze data using software like SPSS, making them both challenging and essential for developing analytical skills. These assignments cover a wide range of topics, from descriptive and inferential statistics to hypothesis testing and regression analysis. To effectively solve such assignments, students need a systematic approach that includes understanding the problem, choosing the right statistical methods, and accurately interpreting results. Missteps such as selecting incorrect tests or misinterpreting data can lead to flawed conclusions. This blog provides a step-by-step guide to tackling statistics assignments with SPSS, helping you solve your SPSS assignment efficiently by focusing on key concepts like t-tests, ANOVA, correlation, and power analysis. By following these structured steps, students can ensure accuracy and clarity in their work, ultimately improving their statistical proficiency and assignment outcomes.
Understanding the Scope of Statistics Assignments

Statistics assignments, particularly those requiring SPSS, often encompass a broad range of topics, including descriptive and inferential statistics, distributions, central tendency, hypothesis testing, power analysis, t-tests, ANOVA, correlation, regression, and non-parametric tests. Successfully solving such assignments requires a systematic approach that ensures a deep understanding of statistical concepts, appropriate application of statistical tests, and accurate interpretation of results.
Key Steps to Solving SPSS-Based Statistics Assignments
1. Comprehend the Assignment Requirements
Before diving into statistical computations, carefully read the assignment instructions. Identify the type of data analysis required, whether it involves descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, or inferential techniques. If the assignment references a specific textbook or dataset, reviewing the relevant sections will provide additional clarity.
2. Understand the Data Structure
Statistics assignments often involve structured datasets with various variables. To efficiently analyze the data:
- Identify dependent and independent variables.
- Determine whether the data is categorical, ordinal, or continuous.
- Recognize sample size implications.
For example, an assignment requiring a comparison between two groups might involve independent or paired samples. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the appropriate test.
3. Conduct Initial Data Exploration
Before performing statistical tests, "eyeball" the data to detect errors, outliers, or anomalies. This step involves:
- Checking for missing values.
- Assessing normality using histograms or QQ plots.
- Identifying potential outliers using boxplots.
For example, if a dataset contains tension and migraine headache intensities, reviewing summary statistics ensures no extreme values distort the analysis.
4. Choosing the Right Statistical Test
Selecting the correct statistical test depends on the nature of the variables and the research question. Some common tests include:
- Descriptive Statistics: Mean, median, standard deviation for summarizing data.
- t-Tests: Comparing means between two independent or paired groups.
- ANOVA: Assessing differences across multiple groups.
- Chi-Square Test: Examining relationships between categorical variables.
- Correlation & Regression: Exploring associations and predictions.
- Non-Parametric Tests: Wilcoxon, Mann-Whitney U tests for non-normally distributed data.
For instance, if an assignment involves comparing headache frequencies before and after biofeedback training, a paired t-test would be appropriate.
5. Performing Power Analysis and Sample Size Calculation
Power analysis helps determine whether a study has enough participants to detect a meaningful effect. If an assignment requires estimating sample size, use the formula based on the type of test being conducted. For example, determining the number of subjects needed in an independent t-test comparing headache intensities may involve:
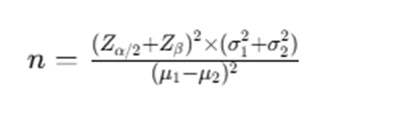
Where σ1 and σ2 are standard deviations, and µ1 and µ2 are means.
6. Conducting Statistical Tests in SPSS
SPSS simplifies running statistical analyses by providing user-friendly menus for computations. Follow these steps:
- Import Data: Load the dataset into SPSS.
- Define Variables: Assign appropriate data types.
- Run Descriptive Statistics: Use "Analyze > Descriptive Statistics" for summary metrics.
- Conduct the Chosen Test: Navigate to "Analyze" and select the appropriate test (e.g., "Compare Means > Independent Samples t-test").
- Interpret Output: Review significance levels (p-values), confidence intervals, and effect sizes.
For example, when analyzing whether headache severity differs between groups, an independent t-test in SPSS will produce output indicating whether the mean difference is statistically significant.
7. Interpreting Results Accurately
Statistical interpretation is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions. Consider the following aspects:
P-values: A result is significant if p < 0.05 (or as specified by the assignment).- Effect Sizes: Measure the magnitude of differences.
- Confidence Intervals: Indicate the range within which true values lie.
- Assumptions Validity: Ensure normality, equal variances, and independence when applicable.
For example, in a power analysis for a study on biofeedback effectiveness, results should indicate whether the sample size was sufficient to detect a significant reduction in headache frequency.
8. Reporting Findings Clearly
Assignments often require detailed reports with:
- Introduction: Outline research questions and hypotheses.
- Methods: Describe datasets, variables, and statistical techniques.
- Results: Present findings with tables, graphs, and numerical summaries.
- Discussion: Interpret the results and their implications.
For instance, when analyzing an ANOVA for headache treatment groups, a well-structured response should explain which groups differ and whether additional post-hoc tests are necessary.
9. Addressing Non-Parametric Alternatives
If data do not meet parametric test assumptions, use non-parametric alternatives:
- Mann-Whitney U test instead of an independent t-test.
- Wilcoxon signed-rank test instead of a paired t-test.
- Kruskal-Wallis test instead of one-way ANOVA.
For example, if headache severity ratings are ordinal, a Mann-Whitney U test would be preferable over a t-test.
10. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Students often make errors such as:
- Misinterpreting p-values.
- Ignoring assumptions of statistical tests.
- Using inappropriate statistical methods.
- Misreporting effect sizes or confidence intervals.
To prevent mistakes, always cross-check calculations, verify assumptions, and follow statistical guidelines.
Conclusion
Solving statistics assignments that involve SPSS requires a structured approach, including understanding the assignment, preparing data, choosing appropriate tests, running SPSS analyses, and interpreting results accurately. To successfully complete your statistics assignment, it is essential to follow each step carefully, ensuring that all statistical tests are applied correctly and data is analyzed accurately. By approaching the assignment methodically, students can minimize errors, avoid misinterpretation, and produce meaningful insights from their analyses. Whether working on t-tests, ANOVAs, or correlation analyses, a careful and thorough approach will lead to more reliable results. Additionally, documenting the findings clearly and logically enhances the credibility of the analysis. With continuous practice and adherence to statistical principles, students can develop confidence in their analytical skills and improve their performance in statistics assignments. Following these systematic steps not only ensures accuracy and precision but also fosters a deeper understanding of statistical methodologies.









