Claim Your Offer
Unlock an exclusive deal at www.statisticsassignmenthelp.com with our Spring Semester Offer! Get 10% off on all statistics assignments and enjoy expert assistance at an affordable price. Our skilled team is here to provide top-quality solutions, ensuring you excel in your statistics assignments without breaking the bank. Use Offer Code: SPRINGSAH10 at checkout and grab this limited-time discount. Don’t miss the chance to save while securing the best help for your statistics assignments. Order now and make this semester a success!
We Accept
- Understanding Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE)
- What is Maximum Likelihood Estimation?
- Steps to Solve MLE Problems:
- Multiple Regression Model and Inference
- What is Multiple Regression Analysis?
- Approach to Solving Regression Assignments:
- Estimating the Average Treatment Effect (ATE)
- Key Steps to Approach ATE Problems:
- Conclusion
Statistical modeling and inference are essential tools in data analysis, enabling researchers and students to draw meaningful conclusions from data. Assignments in this field often involve concepts such as Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), multiple regression analysis, and Average Treatment Effect (ATE). Solving such assignments requires a deep understanding of statistical concepts, rigorous analytical thinking, and the ability to interpret results accurately.

Many students struggle with statistical modeling due to the complexity of formulas, the necessity of programming in statistical software, and the requirement to justify every decision made in analysis. If you find yourself thinking, "How can I complete my Statistical Modeling Assignment effectively?", this blog will serve as a structured guide to help you navigate such challenges. We will provide a clear breakdown of essential techniques and methodologies, ensuring that theoretical understanding is emphasized. Our discussion will focus on core concepts, guiding students through problem-solving approaches, and offering insights into how to interpret results effectively without getting lost in computations. By following this structured approach, you can confidently tackle your statistical modeling assignments with clarity and precision.
Understanding Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE)
MLE is a fundamental method used to estimate parameters of a statistical model. It relies on maximizing the likelihood function, which quantifies how well a parameter explains the observed data by determining the probability of obtaining the given sample. This method is widely utilized in statistical modeling because it provides estimates that exhibit desirable properties, such as asymptotic efficiency and consistency, ensuring reliable parameter estimation as the sample size increases. MLE is particularly advantageous in scenarios where traditional estimation methods fail, allowing for greater flexibility in model specification. It is extensively applied across various fields, including econometrics, machine learning, and biostatistics, due to its robustness and adaptability. The method is also useful in deriving confidence intervals and hypothesis tests for estimated parameters, making it a cornerstone technique in inferential statistics. Its ability to provide optimal estimates in complex modeling scenarios makes it indispensable in modern statistical analysis.
What is Maximum Likelihood Estimation?
MLE is a parametric estimation technique where we select a parameter value that maximizes the probability of observing the given sample data. The assumption behind MLE is that the observed data follows a particular distribution, such as normal, exponential, or Poisson. The likelihood function, denoted as , represents the probability of obtaining the observed data given the parameter . The MLE is obtained by maximizing this function.
Steps to Solve MLE Problems:
1. Identify the Probability Distribution:
- Read the problem statement carefully to determine the assumed probability distribution (e.g., exponential, normal, or Poisson).
- Recognize the Probability Density Function (PDF) or Mass Function given in the problem.
- Understanding the properties of the chosen distribution helps in setting up the likelihood function correctly.
2. Construct the Likelihood Function:
- Use the given data points to write the likelihood function as the product of the PDF values for each observation.
- The likelihood function for independent observations X1, X2,…, Xn is given by:
- Often, the log-likelihood function is preferred since it simplifies differentiation and avoids numerical issues when computing very small probabilities.
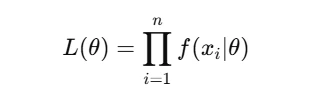
3. Differentiate and Solve for the Parameter:
- Take the derivative of the log-likelihood function with respect to the parameter of interest.
- Set the derivative equal to zero and solve for the parameter estimate.
- If necessary, check second-order conditions to confirm whether the obtained value maximizes the likelihood function.
4. Interpret the Results:
- Evaluate whether the estimate makes sense within the context of the problem.
- Consider asymptotic properties such as unbiasedness and efficiency.
- If the problem provides confidence intervals or variance estimates, interpret their implications.
Multiple Regression Model and Inference
Regression analysis is crucial in statistical modeling, allowing the examination of relationships between a dependent variable and multiple independent variables. It is widely used in economics, social sciences, finance, and business analytics to understand factors influencing a particular outcome.
What is Multiple Regression Analysis?
Multiple regression extends simple linear regression by incorporating multiple explanatory variables to predict the dependent variable. The general form of a multiple regression model is:

Approach to Solving Regression Assignments:
- Understanding the Regression Model:
- Identify the dependent variable and independent variables.
- Determine the expected relationships based on theoretical background.
- Running the Regression:
- If using software like R, Excel, or Python, execute the regression function to obtain coefficient estimates.
- Ensure correct data input, as incorrect specifications lead to misleading results.
- Assessing Statistical Significance:
- Examine p-values for each coefficient to determine individual significance.
- Apply the 5% significance level (if p-value < 0.05, the variable is significant).
- Consider alternative significance levels in specific cases.
- Joint Significance and Model Refinement:
- Conduct an F-test to evaluate whether a group of independent variables collectively impact the dependent variable.
- Modify the model by adding or removing variables based on significance tests.
- Check for interaction effects if necessary.
- Interpreting Coefficients:
- Analyze the sign and magnitude of coefficients to determine their real-world implications.
- Consider the impact of omitted variables and potential multicollinearity.
- Correlation and Model Justification:
- Compute correlation between key variables to understand relationships.
- Discuss whether certain variables should be included or excluded from the model.
Estimating the Average Treatment Effect (ATE)
ATE measures the causal impact of a treatment variable (e.g., training programs, policy interventions) on an outcome variable.
Key Steps to Approach ATE Problems:
- Simple Regression Analysis:
- Begin with a basic regression where the treatment variable is the only independent variable.
- Interpret the coefficient to understand the raw effect of treatment.
- Multiple Regression Adjustment:
- Add control variables to account for confounding factors.
- Compare the coefficient of the treatment variable before and after adjustment.
- Addressing Non-Random Assignment:
- Recognize that observational data is not randomly assigned like an experiment.
- Use regression adjustment to estimate the treatment effect more accurately.
- Interpreting Results and Comparing Effects:
- Determine whether the adjusted ATE is larger or smaller than the simple regression estimate.
- Consider potential biases and suggest alternative approaches such as Instrumental Variables (IV) if necessary.
Conclusion
Solving assignments on statistical modeling and inference requires a clear understanding of estimation techniques, regression analysis, and causal inference. By following a structured approach—identifying distributions, constructing models, running statistical tests, and interpreting results—students can systematically tackle even the most complex statistical assignments. Seeking Statistics Assignment Help can provide valuable guidance in mastering these techniques, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in problem-solving. Developing strong analytical skills in statistical modeling not only aids in academic success but also prepares students for real-world data analysis and decision-making.









