Claim Your Offer
Unlock an exclusive deal at www.statisticsassignmenthelp.com with our Spring Semester Offer! Get 10% off on all statistics assignments and enjoy expert assistance at an affordable price. Our skilled team is here to provide top-quality solutions, ensuring you excel in your statistics assignments without breaking the bank. Use Offer Code: SPRINGSAH10 at checkout and grab this limited-time discount. Don’t miss the chance to save while securing the best help for your statistics assignments. Order now and make this semester a success!
We Accept
- Understanding the Assignment Requirements
- Setting Up the Regression Model
- Incorporating Interaction Terms
- Incorporating Quadratic Terms
- Calculating Sum of Squares Regression (SSR)
- Performing a Nested Model Test
- Model Selection for Prediction
- Practical Steps for Solving Assignments
- Conclusion
Statistical modeling is an essential tool in data analysis, enabling researchers and analysts to understand relationships between variables, make predictions, and test hypotheses. It plays a critical role in various fields, including economics, engineering, business, and social sciences, where data-driven decision-making is essential. Assignments involving multiple regression models, interaction terms, and nested model comparisons are common in statistics courses and require a systematic approach to solving them. To effectively solve your Statistical Modeling Assignments, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and model selection techniques. These concepts help in determining how different variables interact with each other and contribute to the prediction of an outcome. This blog provides an in-depth approach to solving such assignments, ensuring that the methodologies align closely with common statistical problems while maintaining relevance to real-world data analysis applications without being overly generic.
Understanding the Assignment Requirements

Before beginning any statistical modeling assignment, it is crucial to analyze the problem statement carefully. Many assignments involve the following key components:
- Multiple Regression Models: These models establish relationships between a dependent variable and two or more independent variables.
- Interaction Terms: These are used to explore whether the effect of one predictor on the response variable depends on another predictor.
- Quadratic Terms: These terms help capture potential nonlinear relationships.
- Model Comparison and Validation: This involves assessing different models using statistical tests such as Sum of Squares Regression (SSR), Mean Square Regression (MSR), and Nested Model Testing.
- Hypothesis Testing: This determines whether additional terms significantly improve the model.
By carefully understanding the requirements, students can structure their approach methodically and perform the necessary calculations efficiently.
Setting Up the Regression Model
Regression models aim to quantify the relationship between variables in a dataset. Consider a dataset where the dependent variable Y (e.g., delivery time or sale price) is influenced by two independent variables X1 and X2. The simplest form of multiple regression is:
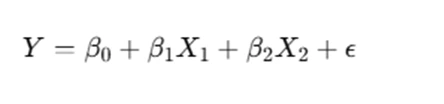
where β0 represents the intercept, β1 and β2 are the regression coefficients for the independent variables, and is the error term.
Incorporating Interaction Terms
In many real-world applications, the effect of one predictor variable may depend on another predictor. To account for this, an interaction term X1X2 is introduced:
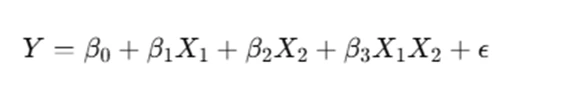
where β3 represents the interaction effect. To determine whether the interaction term significantly improves the model, we compare the sum of squares of the models with and without this term.
Incorporating Quadratic Terms
Sometimes, relationships between variables are nonlinear, meaning that a straight-line relationship does not accurately capture the trend in the data. In such cases, quadratic terms (squared values of predictors) can be added to the model:
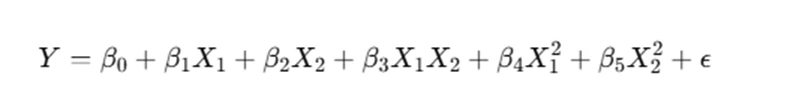
These terms help account for curvature in the data and improve model accuracy.
Calculating Sum of Squares Regression (SSR)
Sum of Squares Regression (SSR) is a measure of how well the independent variables explain the variation in the dependent variable. When calculating SSR for a specific predictor given another predictor, we compare two models:
- Full Model: Includes all predictors (e.g., X1 and X2).
- Reduced Model: Excludes the predictor of interest (e.g., removing X1 while keeping X2).
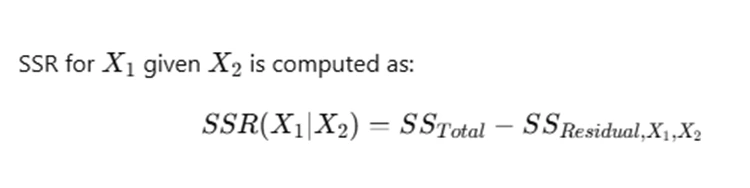
This calculation allows us to assess the contribution of X1 in explaining variations in Y.
Performing a Nested Model Test
A nested model test determines whether a more complex model significantly improves predictions over a simpler one. The null hypothesis typically states that additional terms (interaction or quadratic terms) do not significantly contribute to the model:
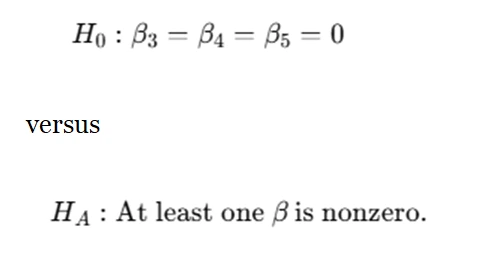
The test statistic is calculated as:
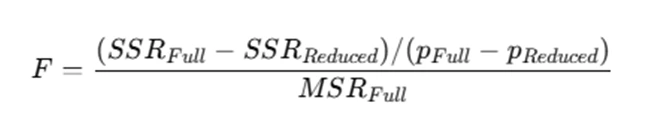
where p represents the number of parameters in each model. A high F-value suggests that the additional terms significantly improve the model.
Model Selection for Prediction
When choosing the best model for prediction, the following criteria should be considered:
- Statistical Significance: If interaction or quadratic terms significantly improve SSR, they should be included.
- Model Simplicity: If adding extra terms does not provide a substantial increase in explanatory power, a simpler model is preferred to avoid overfitting.
- Goodness-of-Fit Metrics: Metrics such as adjusted R2 and Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) help compare models.
- Cross-Validation: Ensuring that the model performs well on unseen data is crucial.
Practical Steps for Solving Assignments
To systematically solve statistical modeling assignments, follow these steps:
- Understand the Dataset: Identify the dependent and independent variables and check for missing values or outliers.
- Visualize Data: Use scatter plots to detect potential linear or nonlinear relationships.
- Fit Basic Models: Start with a simple regression model and gradually add interaction and quadratic terms.
- Compute SSR: Determine the contribution of each predictor and interaction term using sum of squares calculations.
- Perform Nested Model Testing: Compare models statistically to justify including or excluding specific terms.
- Select the Best Model: Use significance tests, adjusted , and other metrics to finalize the model.
- Interpret Results: Clearly explain the impact of each variable and justify the chosen model.
Conclusion
Solving statistical modeling assignments requires a systematic approach that encompasses regression analysis, interaction effects, hypothesis testing, and model selection. To effectively complete your statistics assignment, it is essential to carefully compute the Sum of Squares Regression (SSR), perform nested model tests, and validate models using statistical significance. A structured approach ensures that students can confidently tackle complex problems and justify their findings with strong statistical reasoning. Additionally, understanding the role of interaction and quadratic terms enhances model accuracy and predictive power. Applying techniques such as model comparison, hypothesis testing, and cross-validation helps in selecting the best model while avoiding overfitting. These analytical skills are not only crucial for academic success but also serve as fundamental tools for real-world data analysis across various fields like economics, engineering, and business. By mastering these concepts, students can develop a strong foundation in statistical modeling, making them proficient in handling data-driven decision-making challenges.









