Claim Your Offer
Unlock an exclusive deal at www.statisticsassignmenthelp.com with our Spring Semester Offer! Get 10% off on all statistics assignments and enjoy expert assistance at an affordable price. Our skilled team is here to provide top-quality solutions, ensuring you excel in your statistics assignments without breaking the bank. Use Offer Code: SPRINGSAH10 at checkout and grab this limited-time discount. Don’t miss the chance to save while securing the best help for your statistics assignments. Order now and make this semester a success!
We Accept
- Understanding Control Charts and CUSUM Analysis in Statistical Quality Control Assignments
- Key Components of Control Chart and CUSUM Assignments
- Setting Up a Moving Average Control Chart
- Steps to construct a moving average control chart:
- Interpretation:
- Setting Up an Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) Control Chart
- Steps to construct an EWMA chart:
- Interpretation:
- Setting Up a CUSUM Chart
- Steps to construct a tabular CUSUM chart:
- Interpretation:
- Comparing Control Charts and CUSUM Analysis
- Additional Considerations for Solving Statistical Quality Control Assignments
- Conclusion
Statistical quality control plays a crucial role in manufacturing and process industries, ensuring that products and services meet predefined standards. One of the most effective ways to monitor and improve quality control processes is through the use of statistical control charts. Assignments on this topic often require students to analyze datasets, construct control charts, and interpret the results to determine process stability. These assignments help students develop an in-depth understanding of quality control techniques used in real-world applications.
Control charts, such as the Moving Average Control Chart, Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) Chart, and Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) Chart, are essential tools in process monitoring. These charts help in detecting shifts, trends, and variations in production processes. Understanding how to construct and interpret these charts is fundamental for anyone studying quality control and process optimization. If you need to solve your statistics assignment on control charts and CUSUM analysis, this blog will provide a detailed guide to help you.

Understanding Control Charts and CUSUM Analysis in Statistical Quality Control Assignments
Statistical quality control is an essential aspect of industrial and process control studies. Assignments that require setting up control charts, EWMA charts, and CUSUM charts help students analyze process stability over time. These assignments typically involve monitoring a process where measurements are recorded at regular intervals, and various statistical tools are used to determine whether the process remains within acceptable limits.
Key Components of Control Chart and CUSUM Assignments
Assignments of this nature typically involve:
- Gathering sample data at regular intervals.
- Constructing control charts to monitor trends and variations.
- Applying statistical methods such as the moving average, exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA), and cumulative sum (CUSUM) techniques.
- Analyzing results and interpreting deviations from the expected process target.
Setting Up a Moving Average Control Chart
A moving average control chart smooths out short-term fluctuations in a process by averaging a specified number of past observations. This chart is beneficial for detecting gradual shifts in the process mean.
Steps to construct a moving average control chart:
- Determine the number of past observations (window size, w) used in the moving average calculation.
- Compute the moving average for each observation by taking the mean of the last w values.
- Plot the moving averages over time to visualize trends.
- Compare the plotted values against control limits to detect shifts.
Interpretation:
- If all points remain within control limits, the process is stable.
- If a trend or sudden change is observed, an investigation is needed to identify process issues.
Setting Up an Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) Control Chart
EWMA charts weigh recent observations more heavily than older ones, making them effective in detecting small shifts in the process mean.
Steps to construct an EWMA chart:
- Choose a smoothing constant (λ), typically between 0.05 and 0.2.
- Compute the EWMA value for each sample using the formula:
 is the current observation, and Zt-1 is the previous EWMA value.
is the current observation, and Zt-1 is the previous EWMA value. - Determine control limits based on a multiple (L) of the estimated standard deviation.
- Plot the EWMA values against control limits.
Interpretation:
- Points remaining within control limits indicate process stability.
- A sustained shift may suggest a process change requiring investigation.
Setting Up a CUSUM Chart
The cumulative sum (CUSUM) chart is particularly useful for detecting small shifts in the process mean by accumulating deviations from a target value.
Steps to construct a tabular CUSUM chart:
- Define the reference value k, typically set at half the expected shift.
- Choose the decision interval h to control false alarms.
- Compute cumulative sums for positive and negative deviations:
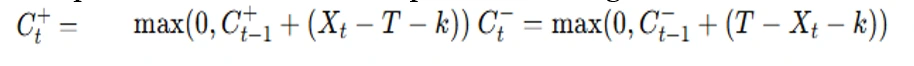 where is the process target value.
where is the process target value. - Plot the CUSUM values over time.
Interpretation:
- If the CUSUM values remain below the decision threshold, the process is stable.
- A steady increase indicates a shift in the mean that requires further investigation.
Comparing Control Charts and CUSUM Analysis
Each method used in statistical process control assignments has specific strengths:
- Moving Average Charts:
- Ideal for detecting moderate shifts in process behavior.
- Helps smooth out fluctuations for better trend visualization.
- EWMA Charts:
- Best suited for identifying smaller shifts due to exponential weighting.
- Gives more weight to recent data, making it more responsive to process changes.
- CUSUM Charts:
- Highly effective in identifying persistent small shifts in process performance.
- Provides a cumulative view of deviations, making it easier to detect trends over time.
By analyzing the results from different charts, students can gain a deeper understanding of process stability and potential sources of variation.
Additional Considerations for Solving Statistical Quality Control Assignments
- Choosing the Right Chart
- Use moving average charts when dealing with processes that exhibit moderate fluctuations.
- Use EWMA charts for processes where recent observations should have a higher impact on decision-making.
- Use CUSUM charts when early detection of small shifts is critical to maintaining quality control.
- Ensuring Accuracy in Calculations
- Double-check moving average and EWMA calculations to ensure correct values are used in plotting.
- Verify standard deviation estimates before setting control limits.
- Make sure the correct parameters (h, k, λ) are used based on assignment specifications.
- Analyzing and Interpreting Results
- Ensure control limits are correctly computed and applied.
- Identify any trends or outliers that suggest process deviations.
- Provide clear and well-supported conclusions on process stability.
Conclusion
Solving assignments that involve constructing control charts and CUSUM analysis requires a structured approach. By understanding the principles behind moving averages, EWMA, and CUSUM methods, students can effectively monitor process stability and detect shifts. These techniques are fundamental in statistical quality control and provide valuable insights into maintaining consistent process performance.
Control charts and CUSUM analysis are widely used in quality management to ensure processes remain within control. Mastering these techniques helps students develop analytical skills that are essential in industrial and business applications. By applying statistical control methods accurately and interpreting results effectively, students can gain a strong foundation in process monitoring and quality control, equipping them with the skills necessary for real-world problem-solving.








