Avail Your Offer Now
Start the New Year on a stress-free academic note and enjoy 15% OFF on all Statistics Assignments while our expert statisticians handle your work with accuracy, clear explanations, and timely delivery. Whether you’re facing complex statistical problems or tight deadlines, we’ve got you covered so you can focus on your New Year goals with confidence. Use New Year Special Code: SAHRNY15 — limited-time offer to begin the year with better grades!
We Accept
- Understanding Factorial Designs in Statistics Assignments
- Identifying Factors and Their Levels
- Conducting ANOVA in SPSS for Factorial Design Assignments
- Interpreting ANOVA Results
- Common Errors in Interpreting ANOVA Results
- Conducting Post Hoc Analysis
- Creating APA-Formatted Figures
- Writing the Results Section
- Example Results Write-Up
- Conclusion
Factorial design assignments in statistics often involve the analysis of multiple independent variables and their interactions. These assignments typically require students to determine factorial notation, identify dependent and independent variables, analyze significance using ANOVA, and sometimes conduct post hoc tests. One such example is the type of assignment that involves testing the impact of different conditions on participant responses, similar to the scenarios outlined in the attached assignment.
Understanding factorial designs is essential for students aiming to interpret complex statistical relationships effectively. These designs enable researchers to evaluate the effects of multiple factors simultaneously, which is crucial in fields such as psychology, business, and social sciences. The ability to solve your SPSS assignment efficiently can significantly enhance your analytical skills, providing valuable insights into experimental outcomes.

In this blog, we will explore how to approach and solve such factorial design assignments using SPSS, while ensuring clarity in understanding statistical significance, interaction effects, and hypothesis testing. We will delve deeper into the nuances of factorial design, discuss various statistical considerations, and provide comprehensive guidelines for reporting results accurately. Moreover, we will discuss the importance of checking statistical assumptions and how correct application of factorial ANOVA can lead to more reliable and valid conclusions. By mastering these skills, students can build a strong foundation in data analysis, which is a crucial competency for advanced statistical research and practical applications.
Understanding Factorial Designs in Statistics Assignments
Factorial designs involve two or more independent variables (factors), each with multiple levels. These assignments require identifying whether the design is between-subjects (BS), within-subjects (WS), or a mixed design. The goal is to analyze how different factors influence the dependent variable and whether their interaction is significant.
Identifying Factors and Their Levels
When solving a factorial design assignment, the first step is identifying the factors and their levels. For example, in an assignment involving political campaign advertisements and voter affinity, we might have:
- Factor 1: Advertisement Type (Rationale, Berate Opponent, Contrast Positions) - 3 levels
- Factor 2: Voter Affinity (Weak, Strong) - 2 levels
- Factorial Notation: 3 × 2 factorial design
A second scenario might involve video game exposure and gender, where:
- Factor 1: Activity Type (Video Games, Books/Board Games) - 2 levels
- Factor 2: Gender (Male, Female) - 2 levels
- Factorial Notation: 2 × 2 factorial design
Once factors and levels are identified, we determine if the design is between-subjects (each participant exposed to one condition), within-subjects (each participant exposed to all conditions), or mixed (combination of both).
Understanding these classifications helps determine the appropriate statistical tests and ensures the validity of results.
Conducting ANOVA in SPSS for Factorial Design Assignments
A key component of these assignments is performing a factorial ANOVA in SPSS. The steps to conduct the analysis are:
- Input the Data: Organize data into columns representing factors, levels, and the dependent variable (e.g., voter likelihood or impulsivity scores).
- Define Variables: Assign proper labels to independent and dependent variables.
- Run Factorial ANOVA:
- Navigate to Analyze → General Linear Model → Univariate.
- Assign independent variables as fixed factors and dependent variables appropriately.
- Include interaction effects to assess combined influence.
- Check Assumptions:
- Conduct Levene’s Test for homogeneity of variance.
- Examine normality of residuals.
Interpreting ANOVA Results
After running the ANOVA, results include:
- Main Effects: Significance of each independent variable separately.
- Interaction Effects: Whether combinations of factors significantly influence the dependent variable.
- Effect Size (Partial Eta Squared): Measures the proportion of variance explained by each factor.
If an independent variable is statistically significant (p < 0.05), we may need to conduct a post hoc analysis to determine which specific groups differ significantly from each other.
Common Errors in Interpreting ANOVA Results
Students often misinterpret ANOVA results by failing to distinguish between main effects and interaction effects. It is crucial to examine both separately and to ensure that interaction terms do not override main effects. Additionally, understanding whether an effect is practically significant versus statistically significant helps in drawing meaningful conclusions.
Conducting Post Hoc Analysis
If a factor has more than two levels and shows significance, a post hoc test determines which specific group differences drive the effect. Common tests include:
- Tukey’s HSD: Compares all pairwise group means.
- Bonferroni Correction: Controls for Type I errors.
- Scheffé’s Test: Useful for complex comparisons beyond simple pairwise tests.
For instance, if advertisement type shows significance, Tukey’s HSD can compare voter likelihood between the three ad types. Choosing the right post hoc test depends on the research question and the structure of the data.
Creating APA-Formatted Figures
After statistical analysis, students must present results in APA format. Steps include:
- Generating Graphs in SPSS:
- Navigate to Graphs → Chart Builder.
- Select an appropriate plot (e.g., bar chart with means).
- Formatting the Figure:
- Label axes properly (e.g., "Voter Likelihood (%)").
- Number the figure (e.g., "Figure 1").
- Add a note explaining the results.
Visual representation of data helps in clearly illustrating trends and significant findings, making it an essential part of statistical assignments.
Writing the Results Section
A professional results section should follow APA guidelines, reporting:
- Statistical Notation: Include F-values, degrees of freedom, and p-values.
- Effect Size Interpretation: Explain significance and real-world implications.
- Post Hoc Findings: If applicable, highlight significant group differences.
Example Results Write-Up
A 3 × 2 factorial ANOVA was conducted to examine the effects of advertisement type and voter affinity on voting likelihood. Results showed a significant main effect of advertisement type, F(2,36) = 4.25, p = 0.02, 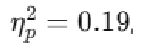 indicating that voter support varied based on ad type. However, voter affinity did not show a significant main effect, F(1,36) = 2.15, p = 0.15. There was no significant interaction effect, F(2,36) = 1.05, p = 0.36. Post hoc tests using Tukey’s HSD indicated that the Rationale ad generated significantly higher support compared to the Contrast ad (p = 0.01).
indicating that voter support varied based on ad type. However, voter affinity did not show a significant main effect, F(1,36) = 2.15, p = 0.15. There was no significant interaction effect, F(2,36) = 1.05, p = 0.36. Post hoc tests using Tukey’s HSD indicated that the Rationale ad generated significantly higher support compared to the Contrast ad (p = 0.01).
Conclusion
Factorial design assignments require a structured approach, beginning with identifying factors and levels, determining factorial notation, and understanding the type of design—whether between-subjects, within-subjects, or mixed. The next crucial step involves conducting ANOVA in SPSS, performing post hoc tests when necessary, and presenting findings in APA format. By following these steps carefully, students can efficiently analyze interactions and main effects, ensuring accurate and comprehensive statistical interpretations in their assignments.
Developing proficiency in these techniques not only helps in solving assignments but also strengthens analytical skills crucial for research and data-driven decision-making. As statistical software like SPSS continues to evolve, the ability to apply factorial analysis effectively becomes even more valuable. Practicing these methods allows students to complete their statistics assignment with precision, enhancing their understanding of experimental designs. Gaining expertise in statistical analysis prepares students for more advanced research, making them confident in handling complex datasets and drawing meaningful conclusions.









